Machine learning (ML) is to train a machine so that it can make decisions for us. This can be achieved by expert system or machine learning.
Expert system is a computer system that emulates the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert system are also known as Rule Based Systems. It emulates how a human makes a decision. Humans look at inputs (features) and then based on previous experience, decide the output. For example an expert system for disease diagnosis will use a fact database and then use the if-then statements to infer the disease from symptoms.
For many well defined problems, expert systems are sufficient but it has problem in various practical scenarios. In cases, where either the parameters to take decision are too many or parameters are not interpretable in machine format, expert systems can not be used and we need another system.
Machine Learning (ML) is the technique of making computer derive these decisions by looking at the data
A machine learning system comprises of parameters that model the problem. Machine is given with a set of data and asked to find a model that best explains the relation between input and output. This model is then used to determine the output of new data.
The current systems are based on mapping as shown below.
𝑦=𝑓(𝑥,𝑤)
Where 𝑥 is input, 𝑤 are the parameters and 𝑦 is the output.
The learning process tries to find a set of parameter values 𝑤 such that the mapping is correct for the majority of cases. If 𝑥 are symptoms then 𝑦 should be the associated disease. In (supervised) machine learning input-output pairs are provided for learning.
In summary, an expert system uses if-then statements when doing inference while an machine learning system projects the input into the model space.
Machine Learning Constructs
Machine learning has lot of jargons. It becomes very confusing and most of the new comers loose direction. Here is a good framework to organize various things in different categories:
- Data — Fuel of Machine Learning.
- Task — Concise definition of input and output.
- Models — Mathematical formulation of a task.
- Loss Functions — Determines which model is better.
- Learning Algorithm — Way to identify the parameters of the model.
- Evaluation — Provides a score to ML model.
Data is everywhere and it plays a very important role in ML. Just having lots of data does not make it useful for ML. Data needs to be in specific format to be useful for ML.
In supervised machine learning, data should be in the format (X, Y) where X is the input for determining the output (Y). These outputs are also known as Labels. Given enough data with (X, Y), ML algorithms can learn the relationship between input and output so that given new input, machine can predict the output.
Data should be in machine readable format i.e. all data is encoded as numbers. Data could be images, text or anything else but these has to be represented in number e.g. pixel values for representing image. Also, this data is generally high dimensional.
Data collection is a big and tedious part of ML. There are various ways to collect or generate data:
- Open source: Google AI, Open Government data Platform India, UCI machine learning repository etc.
- Crowd sourcing: Amazon Mechanical Turk worker, Dataturks etc.
- Simulation: In some cases, data can be simulated by reusing existing data e.g. create signboard for text detection problem.
Recent advances in ML is attributed to wide availability of data by various open sources.
Task is the concise definition of input and output. Same data can be used to perform various tasks. After collecting the data, next step is to identify the tasks.
For example, on a Facebook page, there is lot of data — there are messages, pictures and videos. There could be several tasks performed using this data. One of the task is to image tagging task. The input for this task is the picture and output is bounding box of the person image and name of the person.
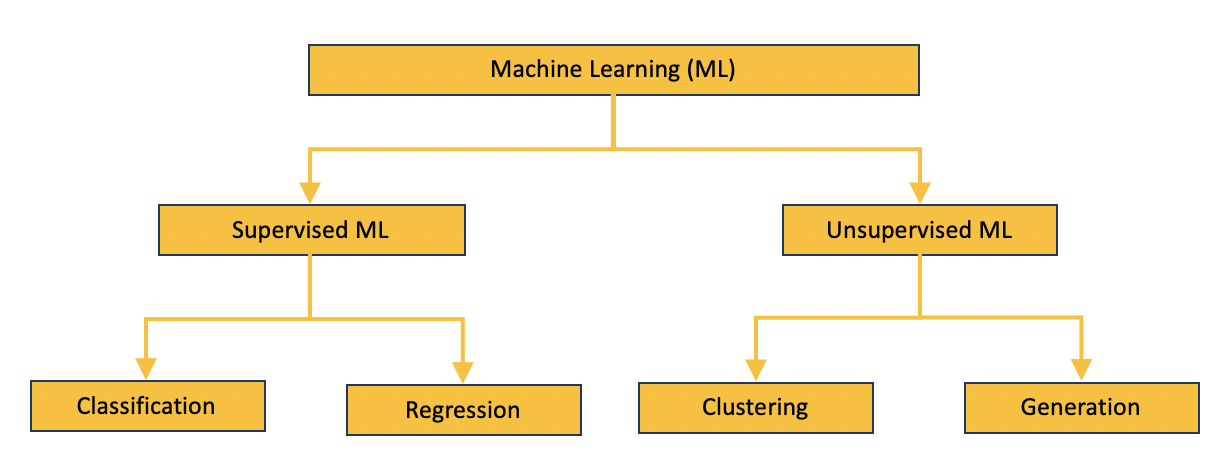
These tasks are organized in two main categories:
-
Supervised Tasks have both input and output data. Two classes of problems that fall in this category are
ClassificationandRegression. Both share the concept of using known datasets (referred to as training datasets) to make predictions. The main difference between them is that the output variable inclassificationis discrete (e.g. Yes/No) while that forregressionis continuous (e.g. identify the coordinates of a picture).Classificationproblems are further divided inbinary classificationandmulti classification. -
Unsupervised Tasks does not have output data (
labels) corresponding to the input data. For example, you can have lot of images but no knownlabels. Two classes of problems that fall in this category areClusteringandGeneration. Clustering identifies similarities between objects, which groups according to common characteristics that differentiate them from other groups of objects. These groups are known as “clusters”. Disadvantage of clustering is that labels are not generated for the clusters by the machine. Generation task is to generate data similar to the input data. For example, given various pictures from known artist, generation can create a new picture similar to the artwork. This task is commonly known as Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs.
Here is a chart that shows the different groupings of machine learning tasks.ml
Model is the mathematical formulation of a task. After task is defined and we have known dataset (X, Y), referred to as training dataset, model is the function so that it maps (models) the input data to the output data. In fact, there are set of functions which are tried to find out the best mapping in known dataset. The function that captures the relationship between X and Y most accurately is the model, which is used to predict the result for the new data.
Models could be very simple or complex function based on the task.
y = mx + c (simple function)
y = m₁₀₀ x¹⁰⁰ + m₉₉ x⁹⁹+ … + m₁ x + c (complex function)
Generally, we begin with simple function and keep increasing the complexity till we find a model which give desired accuracy. While determining the model, following concepts, which will be described in later posts, needs to be considered.
- Bias Variance Tradeoff
- Overfitting
- Regularization
There is one family of functions, neural networks family of functions, which will be described in this series of post:
- Sigmoid / Logistic function
- Deep Neural Network (DNN)
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
- Recurring Neural Network (RNN)
- Various combinations of these functions
Loss functions determines which model is better. It helps to understand how good or bad a model is or how good or bad the current parameters are. Machine automatically estimate the parameters of model and reach the optimal value by minimizing the loss.
In the picture below, we have training data, known (x, y) values. There are three instances of a function with different parameters. Each instance predicts output for each value of x, namely f₁(x), f₂(x), f₃(x). To determine which function predicts the output y correctly, we use square error loss function. In this loss function, each prediction is subtracted with true value, square of the difference is taken and then all of the square differences are added together to get the loss value. In this instance L₁ has the least loss and hence the best approximation of y.
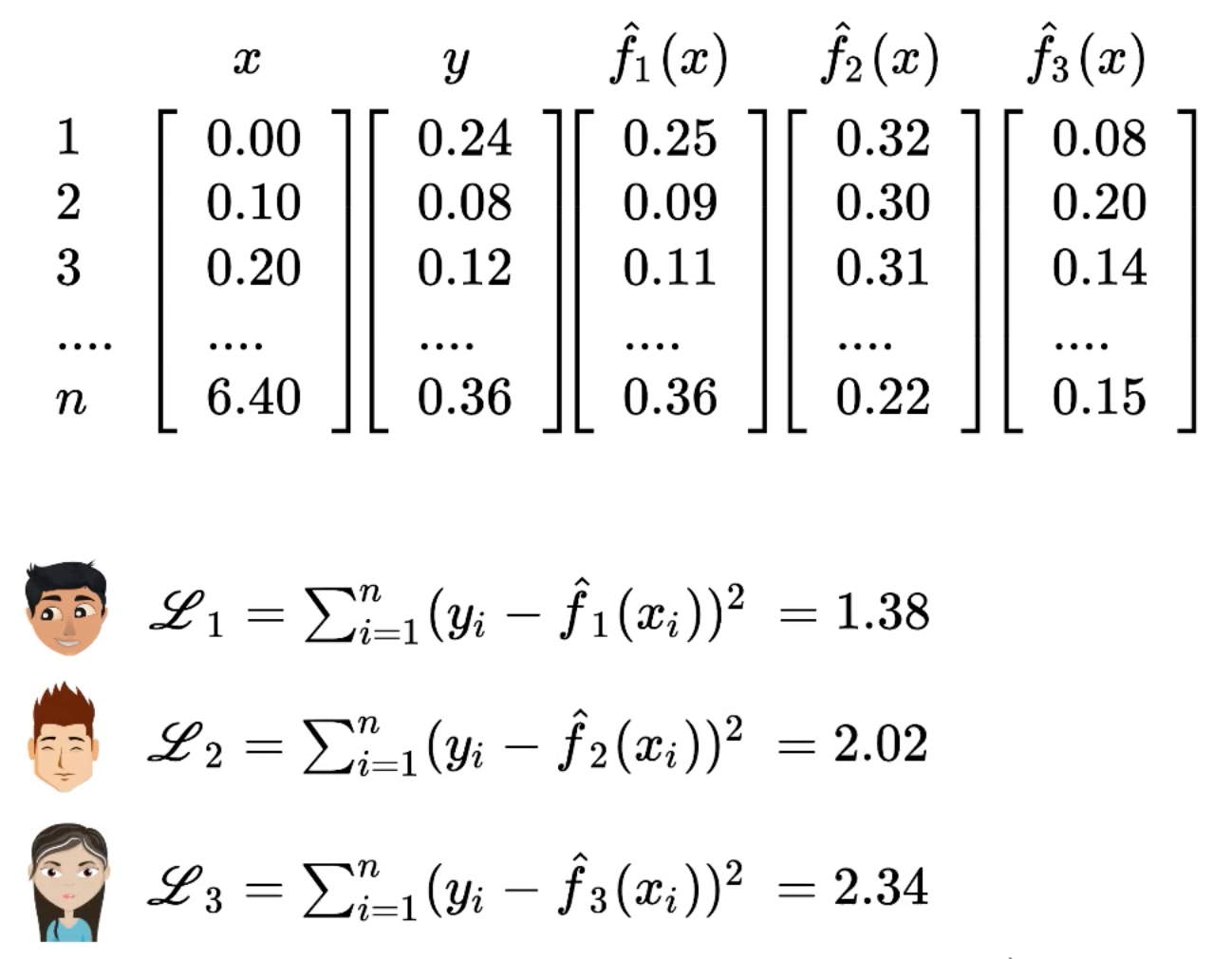
Various loss function discussed in this series are:
- Square Error Loss
- Cross Entropy Loss
- KL Divergence
Learning Algorithms is the way to identify the parameters of the model. In a brute force approach, all combinations of parameters for a model can be tried and using a loss function, we should be able to find the parameters for which loss is minimized. In practice, this is prohibitively expensive as the number of parameters is quite large.
Looking at this problem from mathematical angle, this is an optimization problem. Consider that we have a simple model function and squared error loss, the problem can be written as optimization problem as follows:
Solve
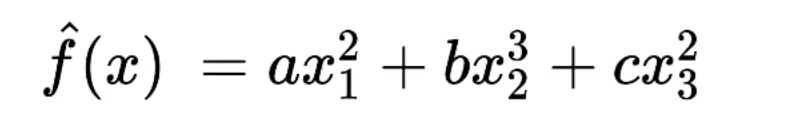
such that
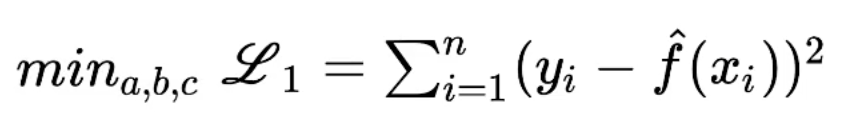
Essentially it means that we want to find (a, b, c) such that loss is minimized.
There are many learning algorithms that are available to solve these problems. We will be looking at:
- Gradiant Descent and it’s variants
- Adagrad
- RMSprop
- Adam
- Back Propagation
- BPTT used for training RNN
Evaluation gives a score to ML model. It tells about the accuracy of the model i.e. how accurately the output predicted by the model is the actual output. In simple terms:
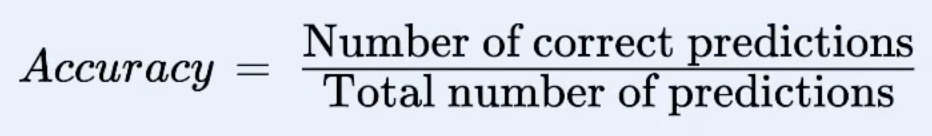
Now, the obvious question is how does evaluation differ from the loss function. To understand it we have to look at precision and recall.
Precision is the number of times correct action is taken out of total number of times action is taken while Recall is the number of times action is actually taken out of total number of times action is supposed to be taken.
These two parameters are used for evaluation. On the other hand, the loss function tries to train the machine to minimize the difference in the output parameter of the model. Hence, evaluation metric and loss function are very different.
Another difference is that loss function uses training data while evaluation uses test data.
Putting it all together
Machine learning is built fundamentally on Mathematics. It heavily uses Linear Algebra, Probability theory and Calculus. Following figure puts all of these together in a neat framework to keep track of so many evolving parts.
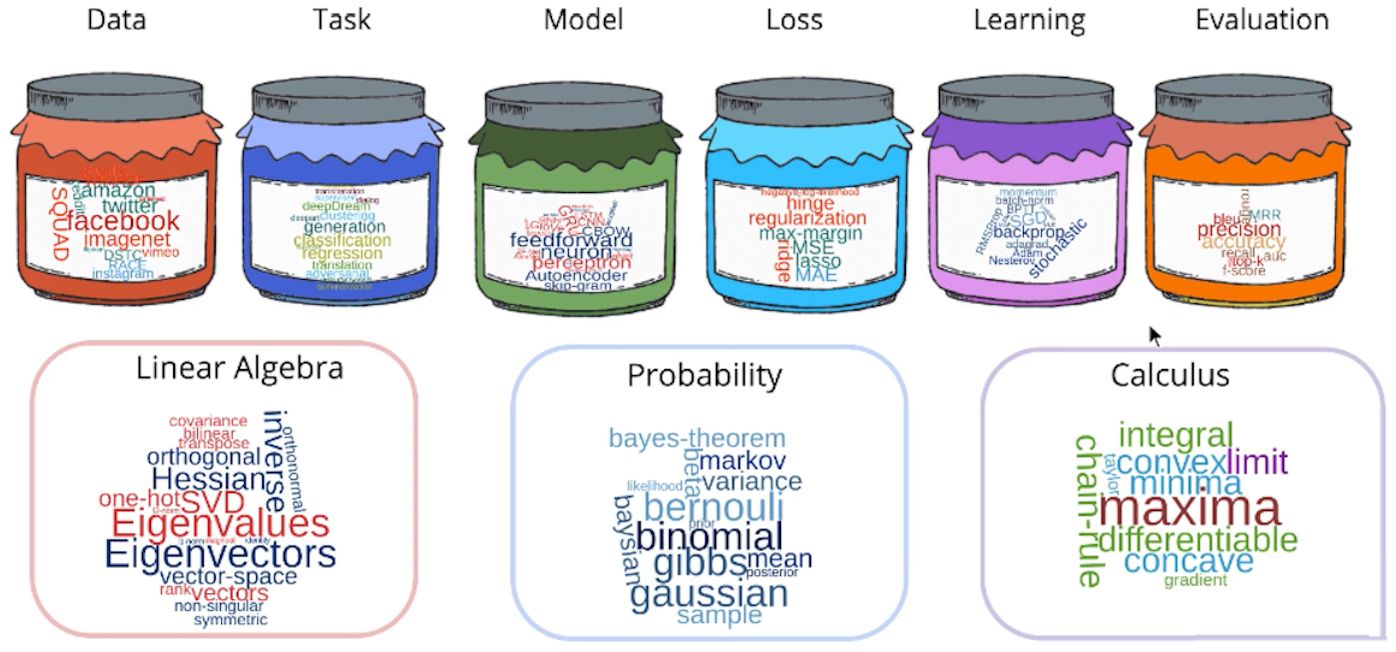
Bottom layer: To understand ML, mathematical concepts are required as these are based on the basic principles of linear algebra, probability and calculus. Doing all of these together is difficult so this framework will help you to approach it in systematic manner.
Top Layer: Out of the six constructs, four constructs have been democratized, improvised and standardized. There are standard evolution metrics provided by PASCAL2 and IMAGENET for problems like image processing, object detection etc. Loss and Learning functions are made available in frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow. Models are democratized as people are publishing their model e.g. LSTM so that everyone can use it. Data is available in abundance on various open platform.
Typical ML effort is to curate data and define the task.
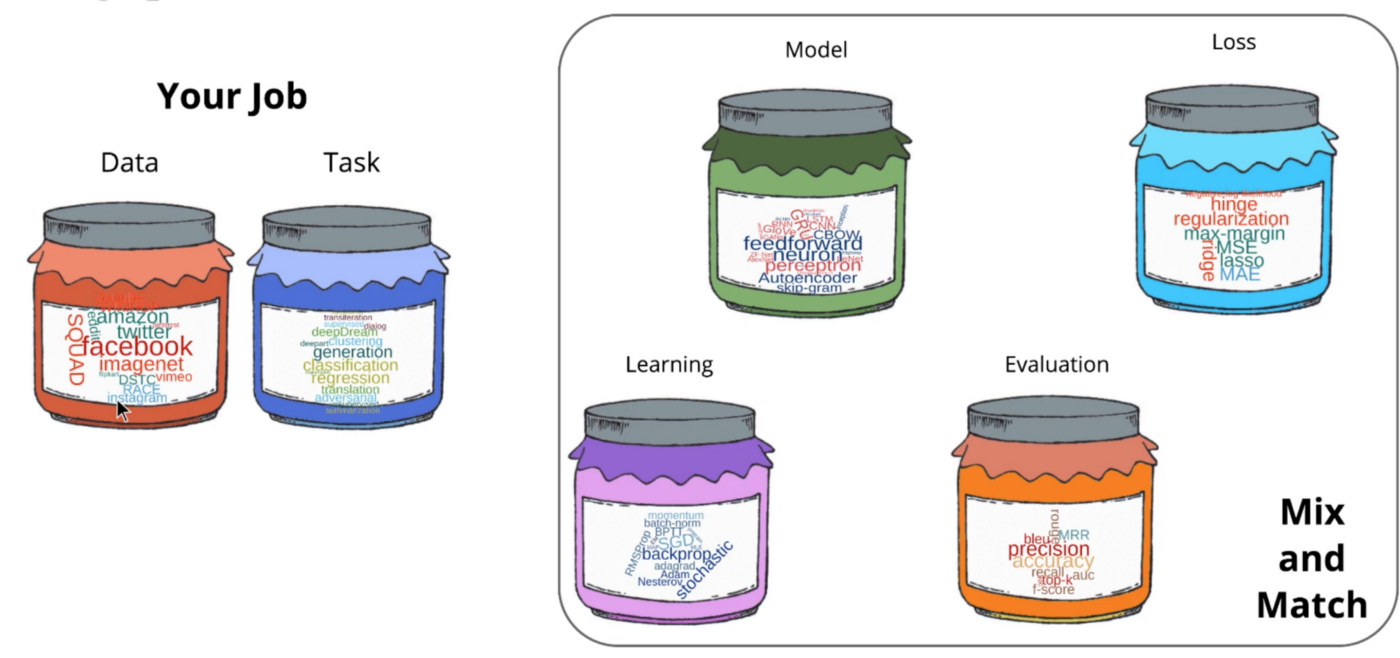
References:
- Deep Learning by One Fourth Labs.