EC2 is one of the most popular AWS offering. It provides the capabilities of:
- Renting Virtual Machines (EC2)
- Storing data on the virtual drives (EBS)
- Distributing load across machine (ELB)
- Scaling a service using auto-scaling group (ASG)
ssh to the instance
Note: Ensure write permission to certificate file (chmod 400 certificate_file)
Using certificate location with CLI
ssh -i ~/certificates/aws.pem ec2user@ec2-instance-url
Alternative add the configuration to ~/.ssh/config
Host my-aws-instance
Hostname ec2-instance-url
User ec2user
IdentityFile ~/certificates/aws.pem
Now use the Host name to ssh
ssh my-aws-instance
User Data
It is possible to bootstrap the instance using user data script. Bootstrapping means launching commands when a machine starts. This script runs only once at the instance first start. It is used to automate boot tasks (e.g. Installing updates, Installing softwares, download common files etc.)
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
AMI is what EC2 instance is based of
AWS comes with base images such as Ubuntu, Fedora, Windows etc. These images can be customized at runtime using EC2 user data. You can create your own image from the instance known as custom built AMIs.
Custom built AMIs have the following advantages:
- Pre-installed packages as needed
- Faster boot time (no need for EC2 user data at boot time)
- Comes with monitoring / enterprise software
- Control of maintenance and upgrade of AMIs over time
- Active Directory Integration out of the box
- Installed app for faster deployment (auto-scaling)
- Using someone else AMIs that is optimized for DB, app etc.
Note: AMIs are built for specific AWS region.
Choosing the right Instance Type
Instances have 5 characteristics advertized on the website:
- RAM (type, amount, generation)
- CPU (type, make, frequency, generation, number of cores)
- IO (disk performance, EBS optimizations)
- Network (network bandwidth, network latency)
- GPU
There are other two categories:
- General Instance (M)
- Burstable Instance (T2)
Refer to Amazon website to choose the right instance carefully.
Network and Security
Security Groups
Security groups acts like a firewall on your EC2 instances. They regulate:
- Access to ports
- Autorized or forbidden IP (ranges) — IPv4 and IPv6
- Control of inbound network
- Control of outbound network
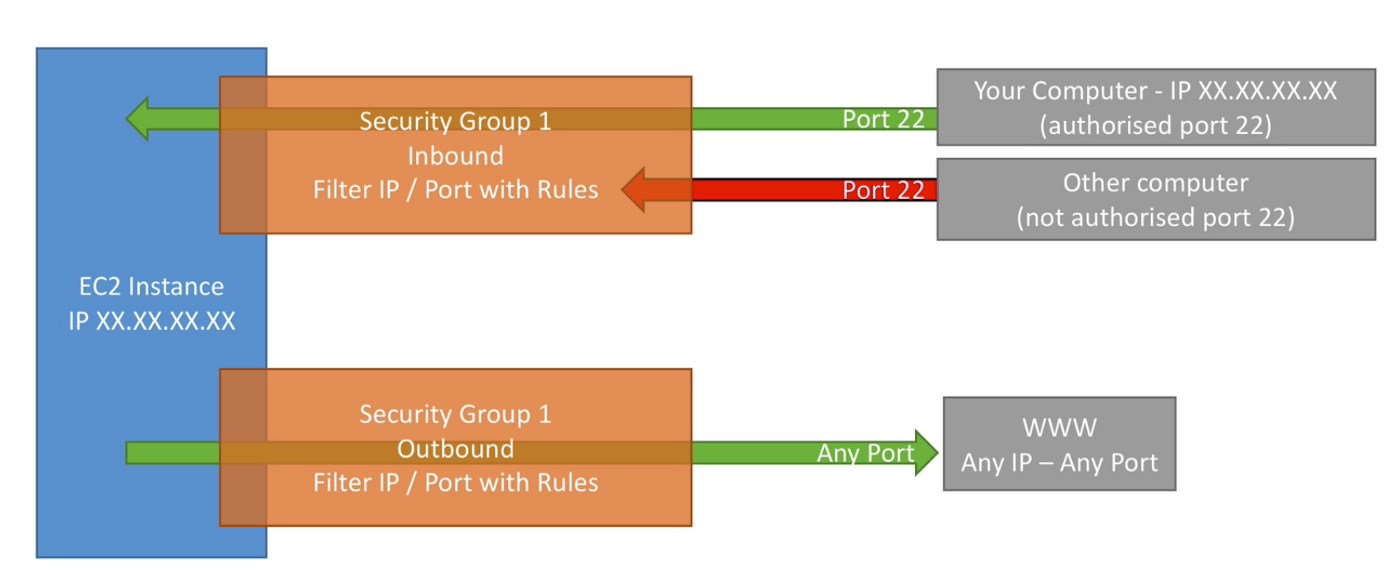
- One security Group can be attached to multiple instances
- Security group is locked down to a region/VPC combination
- Security group live “outside” EC2 instance — if traffic is blocked EC2 instance does not see it.
- All inbound traffic is blocked by default.
- All outbound traffic is authorized by default.
Elastic IPs
An elastic IP is a public IPv4 address which is reserved for your instance. By default, public IP address of instance is not reserved and can change across reboots. One elastic IP is attached to only one instance.
Elastic IP is used to mask the failure of instance by remapping the IP address to another instance of same type.
Avoid Elastic IPs. Instead use DNS.... even better use load balancer so that there is no need of using instance public IP.
Placement Groups
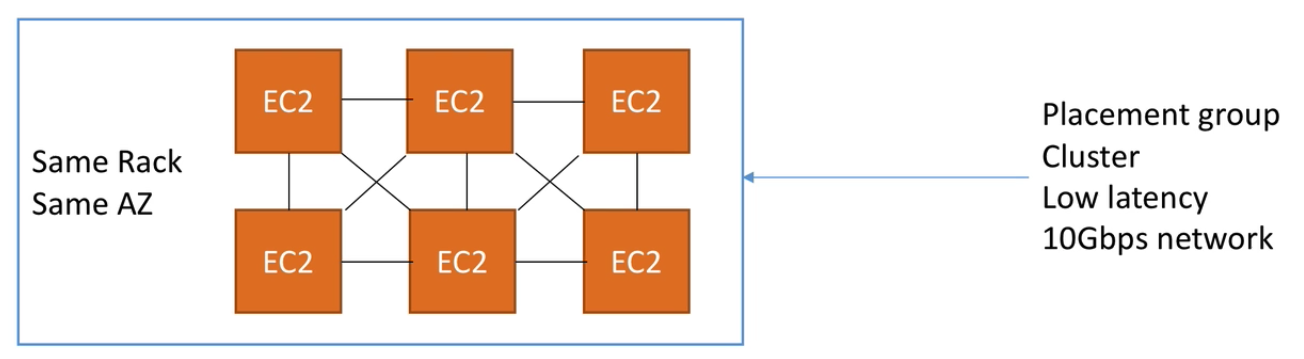
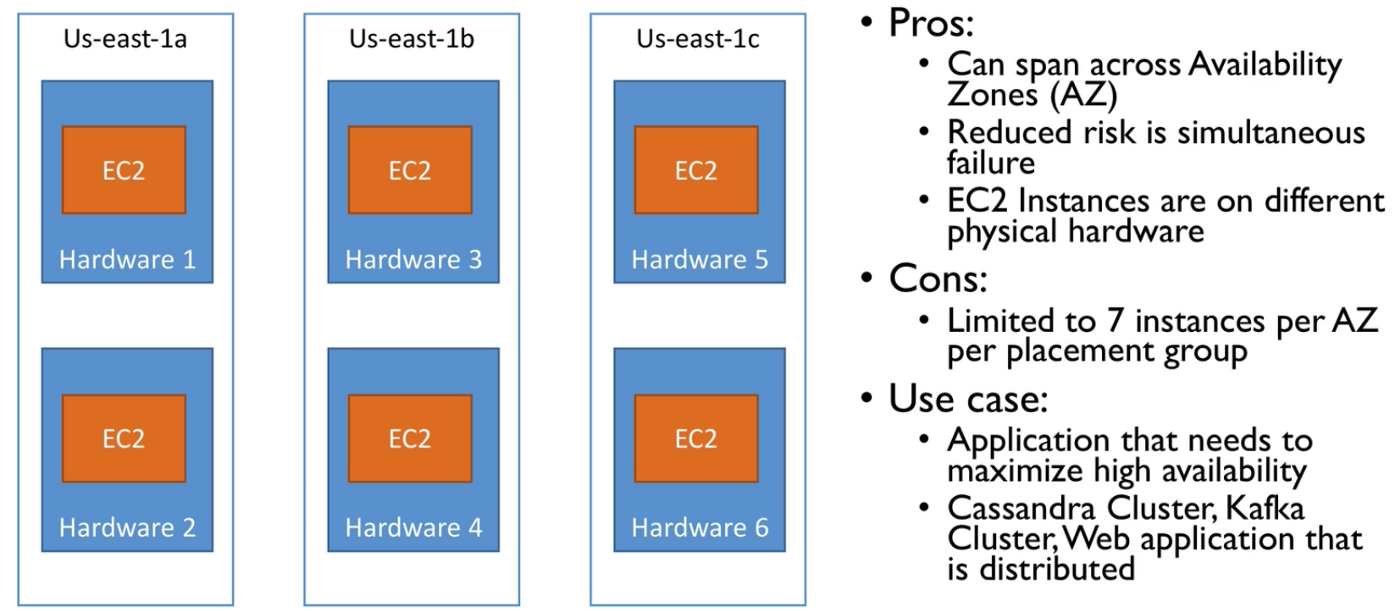
Placement groups provides strategies for placement of EC2 instances. Using placement groups, you can specify one of the following strategy:
- Cluster — clusters instances into low latency group in a single Availability Zone (AZ)
- Spread — spreads instances across underlying hardware (max 7 instances per group per AZ)
Placement groups are not applicable for t2 instances.
Load balancers
There are three types of load balancers
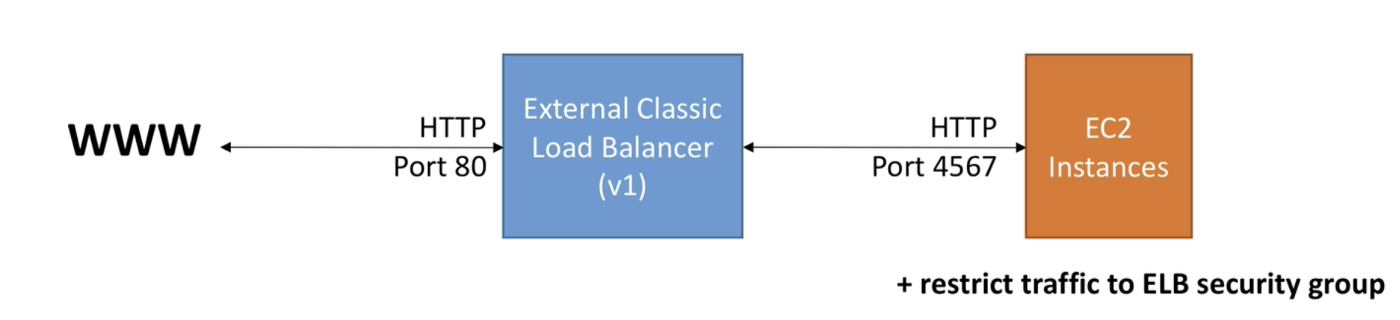
Classic Load Balancer
Many AWS users are still using classic load balancers. They are great to learn the basic concept of load balancing bare are not recommended to use.
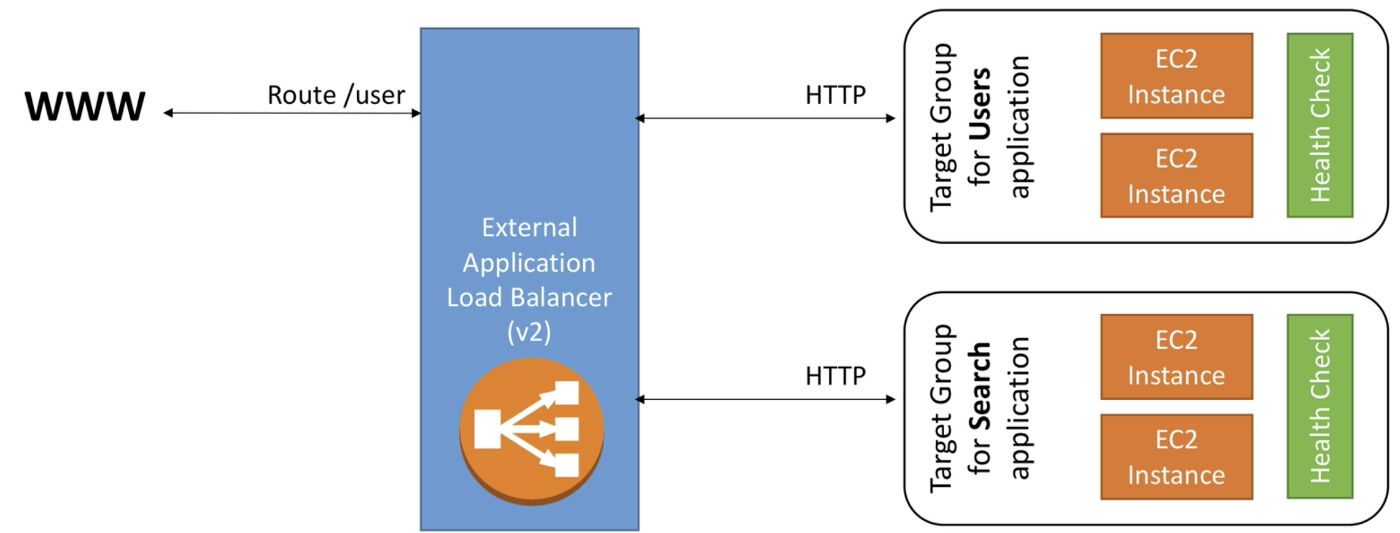
Application Load Balancer (Layer 7)
- Load balancing to multiple HTTP applications across machines (target groups)
- Load balancing to multiple applications on the same machine (ex: containers)
- Load balancing based on route in URL
- Load balancing based on hostname in URL
Basically, they are awesome for micro-services & container-based application (example: Docker). In comparison, we would have to create one Classic Load Balancer per application before, which was very expensive and inefficient.
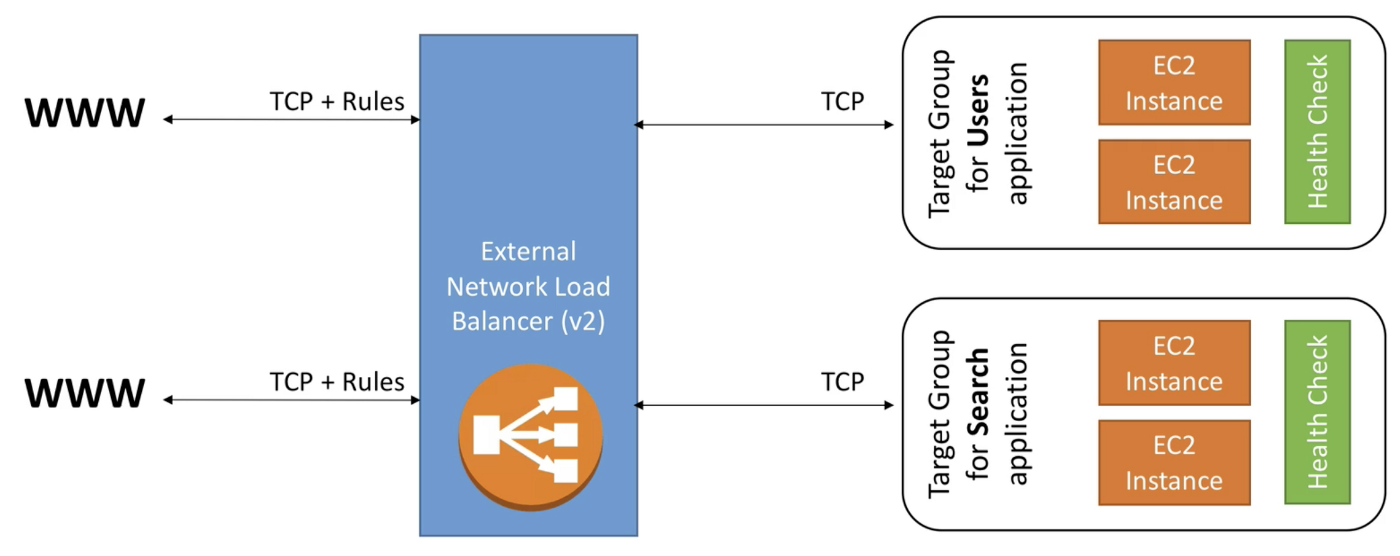
Network Load Balancer (Layer 4)
- Forward TCP traffic to your instances
- Handles millions of request per second
- Support for static IP or elastic IP
- Less latency ~100 ms (vs 400 ms for ALB)
Network Load Balancers are used for extreme performance and should not be the default network load balancer to use.
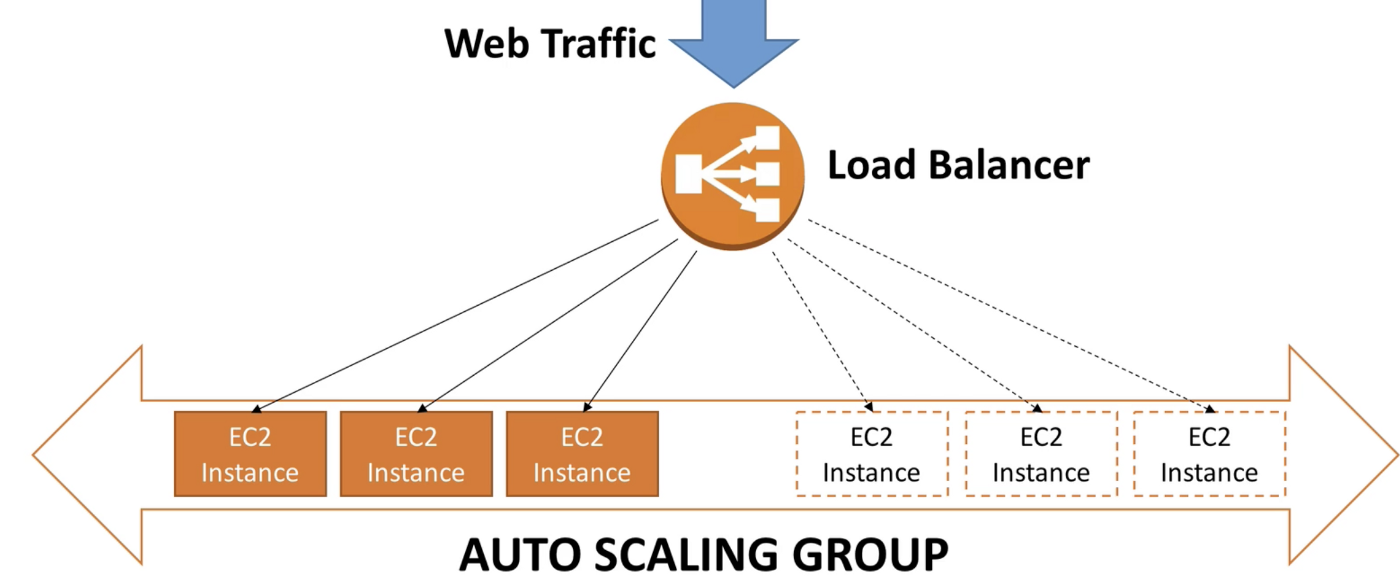
Auto Scaling Application
Automate your application
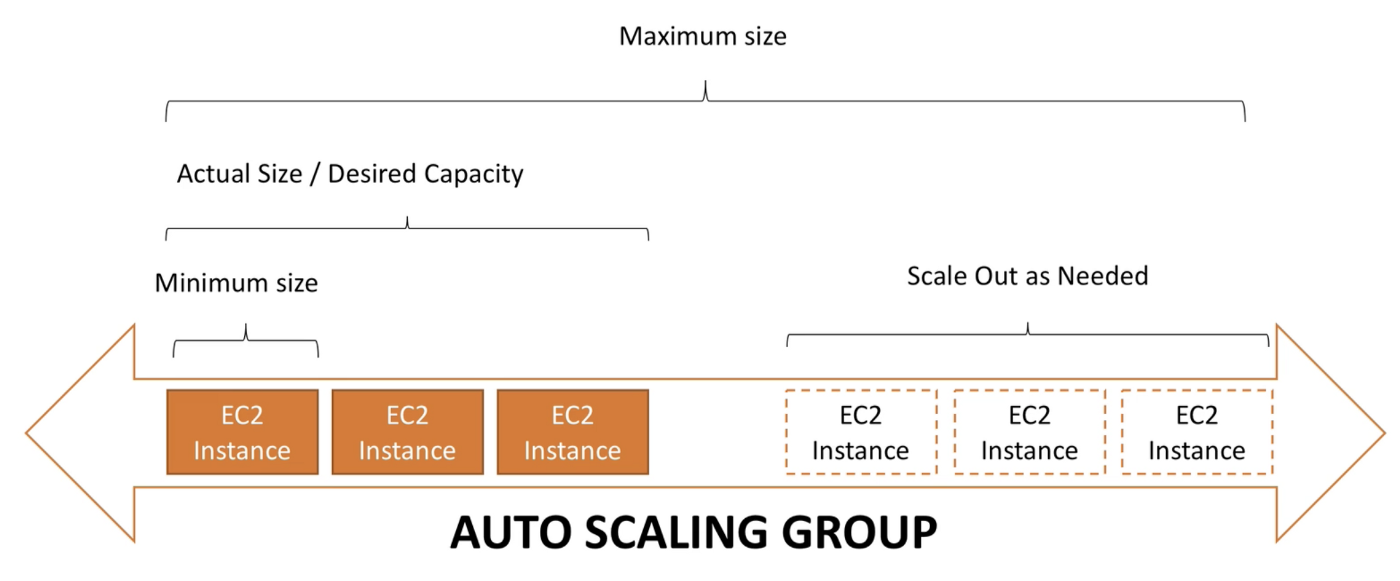
The goal of Auto Scaling Group (ASG) is to:
- Scale out (add EC2 instances) to match increased load
- Scale in (remove EC2 instances) to match decreased load
- Ensure minimum and maximum number of machines running
- Automatically register new instances to load balancer
ASGs have the following attributes:
- Launch Configuration (AMI + Instance type, EC2 user data, EBS volumes, Security groups, SSH key pair)
- Min Size / Max Size / Launch Capacity
- Network + Subnet Information
- Scaling Policies
Auto Scaling Rules
It is now possible to define auto scaling rules that are directly managed by EC2 based on:
- Average CPU Usage
- Number of requests on the ELB per instance
- Average Network In
- Average Network Out
These rules are easier to setup and makes more sense.
Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Store data durably
EBS Volume
EC2 machine loses its root volume when it is terminated but sometimes, you need to store instance data.
An EBS Volume is a network drive that can be attached to the instances when they run. It allows instances to persist data. Main features of EBS volume are:
- It’s a network drive — hence there may be latency. On positive side, it can be detached from an EC2 instance and attached to another one quickly.
- It’s Locked to an availability zone — To move, it needs to be snapshot first.
- It has a provisioned capacity (GBs / IOPS) — Billed for the provisioned capacity.
There are four types of EBS volume:
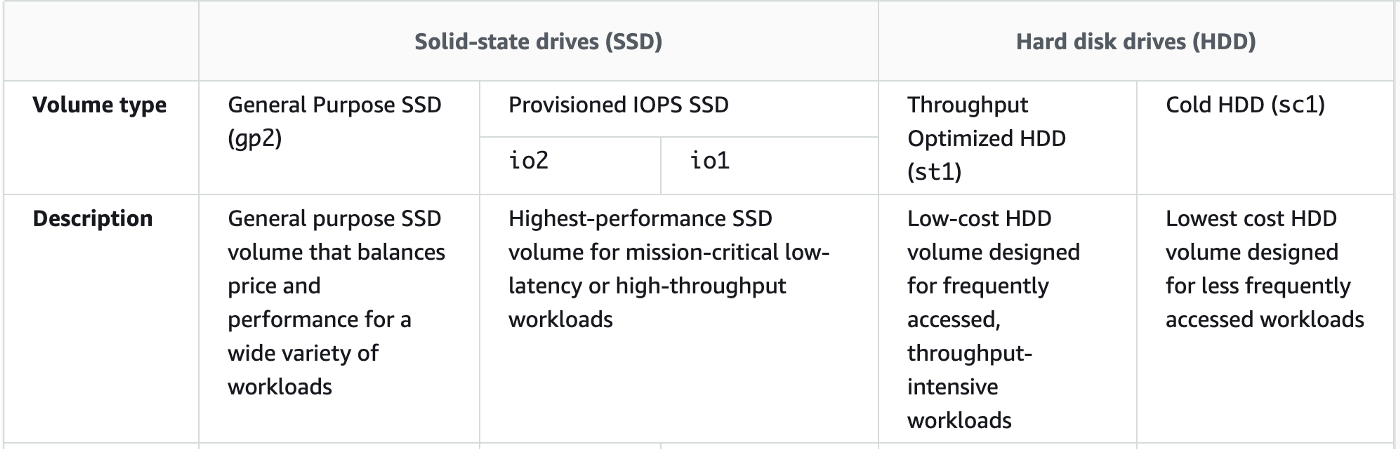
Details can be found at: link
EBS Snapshots
- EBS Volumes can be backed up using “snapshots”
- Snapshots only take the actual space of the blocks on the volume. If you snapshot 1 TB drive that has 50 GB data, then snapshot will be 50 GB only.
- EBS snapshot lives in Amazon S3
- Snapshots are used for backups and volume migration (resizing volume down, changing volume type, changing availability zone).
EC2 Instances Run Modes
Optimize EC2 usage for cost
There are four type of instances:
- On Demand Instances
- Reserved Instances
- Spot Instances
- Dedicated hosts